What is DNS and Why It's Important?
DNS stands for Domain Name System. It works like the internet's phonebook. DNS helps find the IP address of the server hosting the website a user is looking for. When we search for a URL in the browser, the browser sends a query to DNS to get the server's IP address. DNS then contacts the Root name servers, which in turn contact the TLD server (like .com, .net, .in, etc.), and finally, the authoritative server that holds the actual records for the domain name.
How DNS Works?
How DNS Works :
Let's say you want to visit google.com:
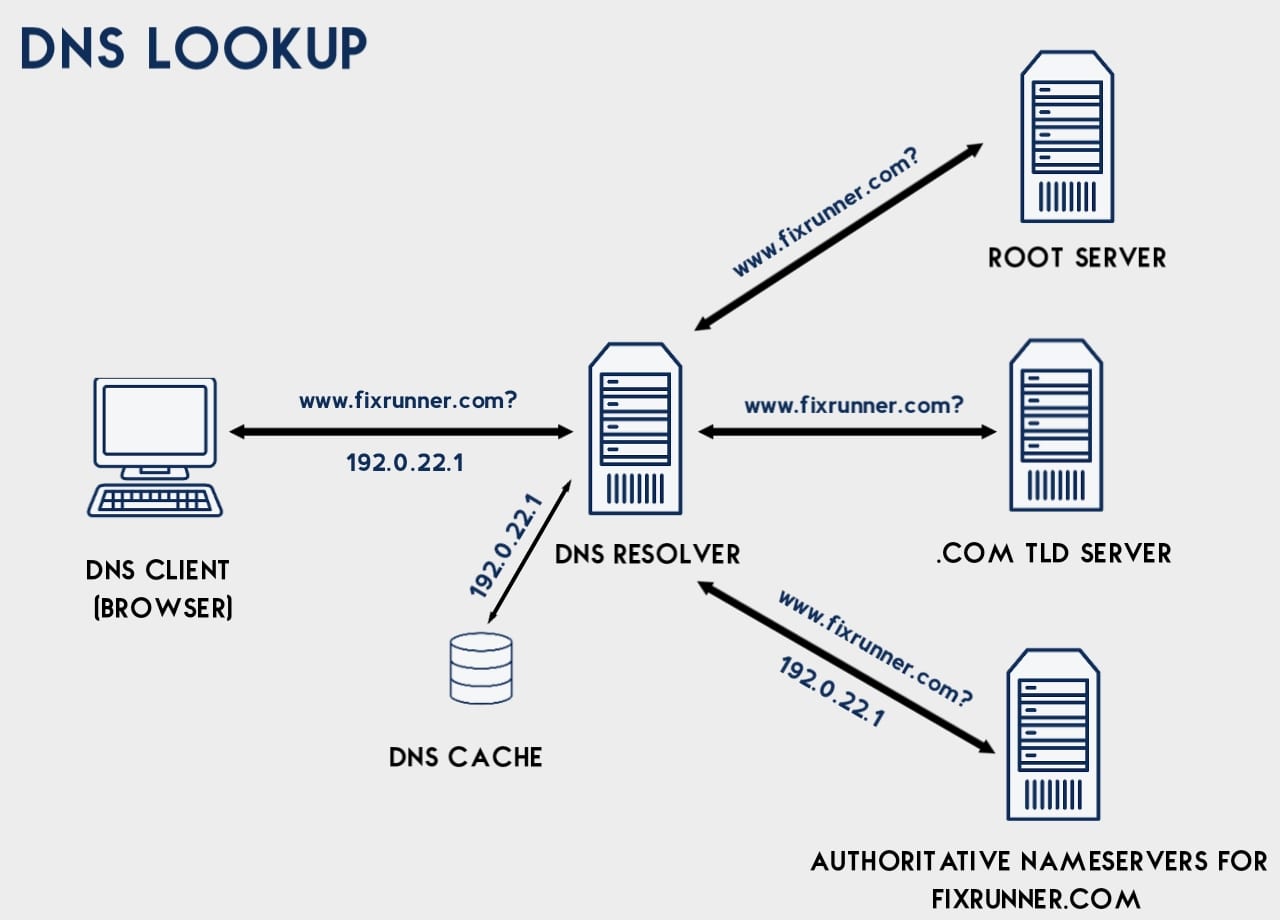
DNS Query Initiation: When you enter google.com in your browser, it first checks if it already knows the IP address (usually from its cache). If not, it sends a query to a DNS resolver.
DNS Resolver: The DNS resolver, often provided by your ISP (Internet Service Provider), starts the process of converting the domain name into an IP address. If the resolver doesn't have the IP address cached, it will query different DNS servers to get the result.
Root DNS Servers: The query is first directed to a root DNS server, which doesn't have the full information but can point to the correct TLD (Top-Level Domain) server based on the domain (for example, for .com, it will refer to .com TLD servers).
TLD DNS Servers: The query then moves to the appropriate TLD server (e.g., for .com domains). The TLD server doesn't have the full domain information, but it will provide the IP address of the authoritative DNS server for google.com.
Authoritative DNS Servers: The authoritative DNS server for google.com holds the specific IP address for google.com (like 192.0.2.1) and sends it back to the DNS resolver.
Returning the IP Address: The DNS resolver now returns the IP address to your browser. With this IP, your browser can now request the web page from the server at 192.0.2.1.
Importance of DNS:
Speed and Efficiency: Without DNS, you would need to remember and enter complex numerical IP addresses for every website you visit. DNS makes the internet more user-friendly and accessible.
Distributed System: DNS is a globally distributed system, meaning it doesn’t rely on a single server. This helps with reliability and resilience of the internet infrastructure.
Security: DNS has some security features like DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) to prevent certain types of attacks, such as DNS spoofing or cache poisoning.